Battery Storage
Battery storage is a specific type of energy storage system that use battery technology to store electrical energy in the battery’s chemical components.
Battery storage can provide individuals and households with resilient back-up power during outages. Homes with solar PV alone do not have power access during an outage. However, a paired energy storage system will allow the home to operate with power (either from stored generation or directly from solar PV generation) even when the electric grid is down.
Battery storage can provide commercial businesses, industry, and manufacturers, as well as public entities with an added revenue stream from participating in local and regional programs and markets. Businesses with strong environmental missions may pair energy storage systems with distributed energy to demonstrate commitment to environmental values and enhance brand image.
Battery storage systems can also provide less costly, grid-beneficial solutions to needs on the electric grid. When sited and optimized, utility-scale energy storage systems can reduce the cost to maintain the electric distribution system and mitigate costs to ratepayers.
How does battery storage work?
Energy storage systems encompass the range of technologies that can store energy at a single location for some amount of time. Battery energy storage systems are a particular subset of technologies that use chemicals to store that energy. Similar to the rechargeable batteries in your phone and power drill, battery energy storage systems can charge up through the electric grid or local clean energy source and later discharge that electricity back to the electric grid or to your home or business.
Figure 1: How batteries work
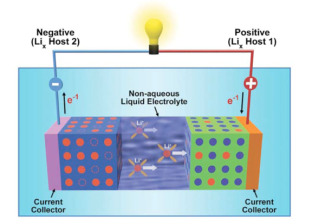
Source: U.S. Department of Energy
As the diagram shows, a battery consists of three basic components: a negatively charged pole (anode), a positively charged pole (cathode), and a material between the two poles (electrolyte). When an electrical current enters the battery, it triggers a reaction within the electrolyte whereby chemicals in the electrolyte capture excess electrons. When the battery is discharged, the reaction is reversed and the chemicals release their electrons, creating an outgoing current.
Programs & Incentives
Customers who pair eligible energy storage systems with small-scale, commercial-scale, and brownfield solar PV can earn additional incentives through the Renewable Energy Fund’s Energy Storage Adder Pilot Program:
Rhode Island Energy customers can earn money for reducing peak demand with their eligible battery energy storage systems:
- ConnectedSolutions – Rhode Island Energy Residential Customers
- ConnectedSolutions – Rhode Island Energy Business Customers
